[unable to retrieve full-text content]
Waverly Labs launches a translation app called Forum with support for 20 languages TechCrunchThursday, February 2, 2023
Opinion | Translating Kafka’s Diaries Reveals a New Side of the Writer - The New York Times - Translation
[unable to retrieve full-text content]
Opinion | Translating Kafka’s Diaries Reveals a New Side of the Writer The New York TimesWednesday, February 1, 2023
This Day in History: Oxford Dictionary Debuts | news.com.au — Australia's leading news site - news.com.au - Dictionary
[unable to retrieve full-text content]
This Day in History: Oxford Dictionary Debuts | news.com.au — Australia's leading news site news.com.auMiss Universe interview question has translation for 'Pang-ilan ka sa magkakapatid?' - Interaksyon - Translation
[unable to retrieve full-text content]
Miss Universe interview question has translation for 'Pang-ilan ka sa magkakapatid?' InteraksyonTuesday, January 31, 2023
Microsoft Research project helps languages survive — and thrive - Microsoft Stories India - Microsoft - Translation
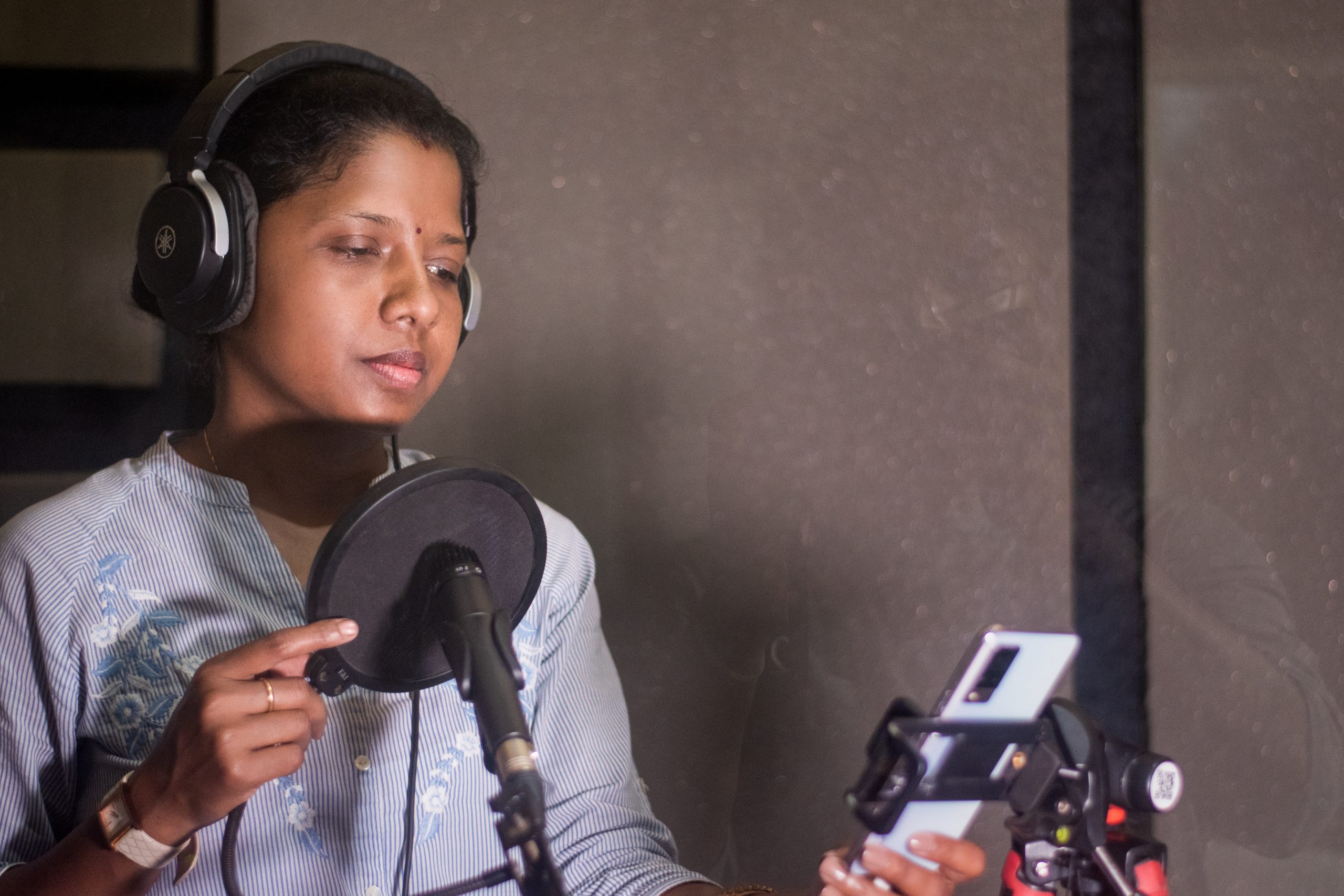
“As a result, the distinction between haves and have-nots became pretty stark,” explains Monojit Choudhury, principal data and applied scientist at Microsoft’s Turing India and Bali’s colleague.
The researchers call languages that do not have resources required to build technology for a digital presence “low-resource languages.”
Under Project ELLORA— Enabling Low Resource Languages — building digital resources has a dual purpose: First, it is a step to preserving a language for posterity; and second, it ensures that users of these languages can participate and interact in the digital world.
Project ELLORA, launched in 2015, began with basics. The first step was to map out what resources were already available, such as printed material like literature and the extent of a digital presence. In a 2020 paper, Bali and her colleagues outlined a six-tier classification, with the top tier representing resource-rich languages like English and Spanish, and the bottom tiers reflecting languages with little-to-no resources.
The work of Project ELLORA is collecting the required resources for these languages and building language models to meet their speakers’ digital needs.
Project ELLORA’s researchers work with the communities to define what this need is and what base technology can help fulfill it. “No language technology can be isolated from the people who are going to use it,” says Bali.
For Mundari, the researchers collaborated with IIT Kharagpur in 2018 and sponsored a study to find what the community needs to keep the language alive.
What started off as a simple vocabulary game for school children to get them to learn the language soon morphed into sophisticated technology projects.
MSR researchers are currently working on a Hindi-to-Mundari text translation as well as a speech recognition model that will provide the community access to more content in Mundari.
A text-to-speech model, funded under the “Forward – Artificial Intelligence for all” initiative by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) on behalf of the German Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development, is also in the works.
But creating language translation models for a language that doesn’t have any significant digital content to train machine learning models is no easy feat.
The team, led by professors of IIT Kharagpur, initially worked with members of the community to have them manually translate sentences from Hindi to Mundari.
To speed the translation, MSR researchers developed new technology called Interneural Machine Translation (INMT), which helps predict the next word when someone is translating between languages.
“It (INMT) allows for humans to translate from one language to another more effectively. If I’m translating from Hindi to Mundari, when I start typing in Mundari, it gives me predictive suggestions in Mundari itself. It’s like the predictive text you get in smartphone keyboards, except that it does it across two languages,” Bali explains.
To build the dataset for text to speech, they collaborated with Karya, which started off as a research project by Vivek Seshadri, a principal researcher at MSR. Karya is a digital work platform for capturing, labeling and annotating data for building machine learning and AI models.
The team identified a male Mundari speaker and Dr. Munda as the female speaker, who were given the translated sentences to record. They recorded the sentences on the Karya app on Android smartphones.
The recordings, along with the corresponding text, are securely uploaded to the cloud and are accessible for researchers to train text to speech models.
“The idea is that between Microsoft Research, Karya and IIT Kharagpur, we will have data for machine translation, speech recognition and text-to-speech synthesis, so that all these three technologies can be built for Mundari,” elaborates Bali.
These connections between language and technology are basic building blocks that eventually could enable sophisticated systems like translation services on government websites or streaming platforms. These systems are already a reality for the language you are reading this article in.